The scorching sun is as hot as fire. The air compressor station is in a mess. Recently, the relevant departments of Xi'an, including the ultrafiltration technology, after-sales service, sales, quality control, etc., held a summer equipment operation summary and exchange meeting. The participants introduced their own practical experiences and feelings in the operation site under the high-temperature conditions of this summer from different perspectives. An in-depth analysis and exchange were conducted on the operation status and countermeasures of our company's dryers, filters, and other related equipment in the air compressor station under the summer high-temperature conditions. After the meeting, the company's general manager Li Daming personally wrote a special article titled "Operation Status and Countermeasures of Purification Equipment in the Air Compressor Station under Summer High-Temperature Conditions".
Abstract: In the summer under high-temperature conditions of the air compressor station, more than half of the air compressors and purification equipment experienced overload and even alarm shutdown. The main reasons for this are as follows: First, insufficient attention was paid to the circulating cooling water system, manifested as insufficient cooling water volume, high water temperature, and deviation in water quality; second, when selecting unit products, the pressure, temperature coefficients, and extreme working conditions were not considered, resulting in an under-sized selection; third, the air compressor factory paid insufficient attention to the end cooler and even cut corners, causing the exhaust temperature of the air compressor to be generally high, with water-cooled units reaching over 45°C and air-cooled units exceeding 55°C. The regulations for the purification industry specify the working conditions: Europe is 35°C, the United States is 38°C, and the industry standards in China have both of these working conditions. Some manufacturing factories, to cope with high-temperature working conditions, set the maximum allowable inlet temperature for adsorption dryers to 40°C, and for refrigerant dryers, the maximum allowable inlet temperature under special design is 45°C.
This paper analyzes the impact of high temperature on the purification equipment of the compressed air station and proposes countermeasures and solutions.
1. Impact of Temperature Environment and Humidity on the Compressed Air System
1.1 Atmospheric conditions (temperature, relative humidity) determine the total water volume entering the air compressor system. In addition, high temperature and high humidity will affect the outlet temperature of the circulating water, thereby determining the liquid water discharge volume of the separator and filter and the absolute moisture content of the saturated moist air entering the dryer (g/m3). It is worth noting that the amount of water vapor entering the dryer is not directly related to the atmospheric conditions, but is a single-valued function of the saturated moist air temperature. Because even when the atmospheric relative humidity is as low as extremely dry 20%, when compressed to 7 bar and cooled to room temperature, a supersaturated moist air has been formed, and the condensed water carried by it is discharged through various separators and filters. Therefore, the factor determining the moisture content吸入量 of the dryer is only the cooling water temperature (for air-cooled units, it is the ambient temperature) and the cooling and separation efficiency (see Figure 1).
1.2 Purification Product Standards and Operating Conditions:
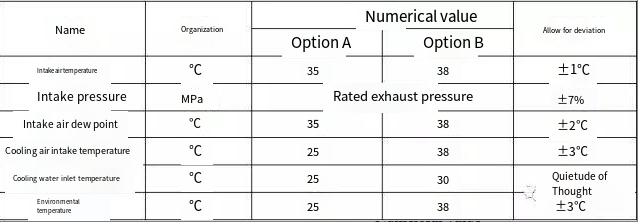
As is well known, no single technology or product can cover all situations. An important aspect of product standards is to specify the applicable scenarios, scope, and related conditions for such products. Generally, the operating conditions for refrigeration-type compressed air dryers (as per JB/T10526-2005) and for general adsorption-type compressed air dryers (as per JB/T10532-2005) are exactly the same (see Table 1). The inlet air temperature is specified in two ways: Scheme A/Scheme B are respectively set at 35°C/38°C. The former is suitable for temperate regions, while the latter is suitable for subtropical regions. Although China has a vast territory, most regions still experience hot summers with high temperatures. The main difference between the north and south is humidity and the duration of high temperatures. Therefore, most production plants have adopted Scheme B, that is, the inlet air temperature is 38°C ± 1°C. As mentioned earlier, the inlet air temperature mainly depends on the cooling water temperature. Considering a temperature difference of about 5°C for heat exchange, the cooling water is specified as 30°C ± 3°C. In actual calculations, 32°C is mostly used. It is worth noting that the specified cooling air inlet temperature and ambient temperature in Table 1 for Scheme B are both 38°C ± 3°C. This value contradicts the inlet air temperature of the dryer at 38°C. In reality, the exhaust temperature of most air compressors with air cooling is 8 to 15°C higher than the ambient temperature. These types of machines become the hardest-hit areas during hot summer conditions.
Table 1: Operating Conditions Specified in Product Standards for Dryers
1.3 The Impact of High Temperature on Adsorption Dryers:
Table 2: Comparison Table of Saturation Temperature and Absolute Moisture Content
From the above table, it can be seen that: when the temperature rises from 38℃ to 48℃, the moisture content increases by 63%; from the "isobaric adsorption graph", it can also be observed that at the working point of the dryer (25-45℃), the isobaric adsorption line is very sensitive to temperature. As the temperature rises, the adsorption capacity of the adsorbent decreases significantly. Combining the above two factors and in accordance with statistical laws, it can be roughly concluded that for every 1℃ increase in temperature, the working load of the dryer increases by about 10%.
Another negative impact of the increase in intake air temperature is that the adsorption heat increases significantly and leads to a substantial increase in the exhaust temperature of the dryer (8-20℃. The higher the intake air temperature, the greater the amount of adsorption heat generated). Since the cooling process mostly uses the product gas from the dryer outlet, this undoubtedly raises the starting temperature of the cooling air, and its temperature can even reach 50-60℃. This inevitably leads to incomplete cooling, and before the cooling process is completed, the temperature of the tower remains as high as 80-100℃. After the switch, the temperature and dew point of the adsorption tower outlet and dew point temperature exhibit severe drift, and the temperature and dew point are generally elevated by more than 20℃, with the duration exceeding half an hour.
1.4 Impact of high temperature on the refrigerated dryer:
The increase in intake air temperature of the refrigerated dryer not only directly increases the heat load of the refrigeration system, but also increases the moisture content in the intake air. When water vapor condenses, the system needs to pay additional latent heat of phase change, and both require providing more cooling capacity or energy consumption; high-temperature gas will also increase the load of the evaporator, possibly causing the dew point of the product gas to increase, resulting in a decrease in the water removal capacity of the refrigerated dryer. In addition, an increase in ambient temperature or cooling water temperature will directly affect the heat exchange efficiency of the condenser, leading to a significant decrease in the system's refrigeration capacity. An increase in condenser temperature will also inevitably cause an increase in condensation pressure. When it exceeds the limit that the equipment can withstand, there is a possibility of equipment and personal safety accidents.
1.5 Impact of high temperature on the oil removal filter:
The product standard for the compressed air filter is being formulated, but in the measurement method (GB/T13277.2-2015) and experimental method (GB/T30475.1~2-2013), the intake air temperature and ambient temperature are both stipulated as 20℃. It is worth noting that the residual oil content indicators provided by the filter manufacturers mostly adopt the performance indicators of the filter element suppliers under 20℃ conditions, while the actual working temperature of the filter is much higher than 20℃. Its residual oil content indicators are several times, even up to 10 times, higher than those provided by the filter manufacturer. (See Table 3)
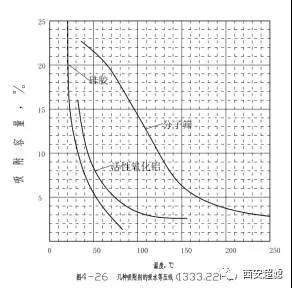
Table 3: Oil/gas ratio of oil separation by spray screw in different temperatures
Although this table does not indicate the absolute oil content, it can be seen that for every 5℃ increase in temperature, the volume of oil vapor doubles. This conclusion is consistent with the statistical data "For every 5℃ increase in temperature, the residual oil content doubles". This is because modern precision/super-precision technologies have an oil-soluble aerosol removal rate of up to 99% - 99.99%. Any filtration method has no effect on gaseous oil vapor.
As the temperature decreases, the oil vapor will condense into liquid oil aerosol, and the oil vapor can also partially deposit on the surface of the adsorbent. Lubricating oil can cause the adsorbent to lose some of its activity, and in severe cases, it can lead to oil poisoning, causing the adsorbent to fail.
2 Strategies
As mentioned above: An increase in intake air temperature will cause the load of the dryer and filter to increase, performance to decline, and even endanger equipment and personal safety. From the statistical data: The exhaust temperature of the air compressor in summer is much higher than the ideal working temperature and specified conditions of the dryer. Therefore, the following three methods can be adopted to remedy or compensate for this situation.
2.1 When the cooling water temperature can be guaranteed to be ≤ 32℃, a low-temperature difference high-efficiency water cooler (the temperature difference between the inlet and outlet water of the cooler is designed to be 3℃) can be added between the air compressor and the adsorption dryer. The temperature difference △t between the inlet and outlet of the cooler is 10℃.
2.2 When there is no cooling water on site or the cooling water temperature itself is higher than 35℃, as above, add a low-temperature difference water cooler. Use chilled water or a self-provided water chiller. The full flow of chilled water or mixed with the circulating water enters the cooler. The temperature difference △t between the inlet and outlet of the cooler is 10 - 15℃.
2.3 The same conditions as above, adopt pre-cooling + adsorption. The pre-cooling machine and the traditional cold dryer have different functions. The former is mainly used for cooling and temperature reduction rather than freezing and water removal, that is, using the refrigerant cooling method to limit the reduction of the compressed air temperature to make it suitable for the adsorption dryer to work effectively within a reasonable temperature range. Currently, this application product belongs to non-standard customization and urgently needs to be standardized to form a series of products.
2.4 Correct selection: When the actual working pressure is low and the working temperature is high, refer to the following correction table:
Table 4: Pressure and Temperature Correction Coefficient Table (DH Sample)
From the table, it can be seen that: based on 7 bar and 35℃, the upward deviation correction value of temperature and pressure is greater than the downward deviation correction value.
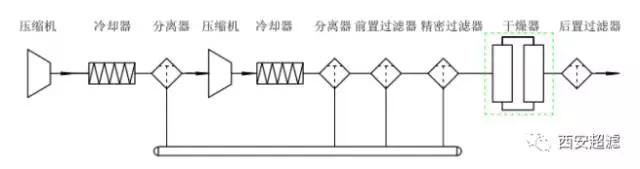
Conclusion: The working temperature range of the dryer and filter should be 25 ± 10℃. Currently, the exhaust temperatures of the in-use and continuously operating air compressors are generally > 40℃. To ensure the normal operation of subsequent purification equipment, the cooling + purification process should be given priority. This method has an essential difference from the traditional cold drying + adsorption method and has better purification indicators and greater investment and operation cost advantages. The recommended sequence of cooling + purification in this article is cooling器 - water cooling unit - pre-cooling machine. The operating conditions and cooling amplitudes of the three are different. As for which method to adopt, it can be selected based on on-site conditions, purification indicators and cost accounting through comprehensive consideration.